Provision maps should be an integral part of the whole-school planning and development process, involving all the staff. They can be used in a number of ways to inform and support the school’s improvement plan, by:
- Auditing how effectively provision (resources, intervention and skills) matches need
- Highlighting gaps in provision
- Accurately costing provision
- Highlighting repetition and ineffective use of resources
- Assessing school effectiveness and value for money when linked with outcomes for pupils
- Planning necessary developments to meet pupils’ identified needs
- Setting annual success criteria for the school’s SEN policy
- Demonstrating accountability
- Informing parents/carers, the local authority, external agencies and Ofsted
- Focusing attention on whole-school issues of teaching and learning
- Recording changes in provision
- Forming the basis for writing individual education plans
Types of provision map
Provision maps can detail the range of additional provision, staffing and support. They can be drawn up according to:
- Class base, year group or Key Stage
- Whole-school inclusion, special educational needs or additional needs
- The SEN code of practice graduated response strands of action: school action, school action plus and statement
- The SEN code of practice four main areas of need: cognition and learning; communication and interaction; emotional, behavioural and social; sensory and physical
- The three ‘waves’ of support as identified in the National Strategies:
- Inclusive quality-first teaching for all
- Additional interventions to enable children to work at age-related expectations or above
- Additional highly personalised interventions
- Costs, either termly or annually
- A combination of any of the above
Developing a provision map
Provision mapping is a process by which the value and effectiveness of provision across the school can be evaluated. It is important that schools view provision mapping as part of a cyclical school improvement process and link it to the school self-evaluation process.
Provision mapping is often described as a jigsaw of four pieces. These pieces are:
- An audit of need
- A comparison with existing provision
- Identify available resources
- Consider what works and plan the provision for next year
The Primary and Secondary National Strategies advise that planning effective provision will involve the four steps below. These are taken from the Leading on Intervention area of the National Strategies website, now available on the Teach Find archive website.
(The National Strategies flowchart on planning effective provision sets out the original seven steps. Two of the steps have since been combined, while the final two steps are now considered 'additional'.)
Planning effective provision: a flowchart, National Strategies on Teachfind (PowerPoint ppt file)
http://nso.archive.teachfind.com/downloader/c72be352c815a1dfd55266f52a14a761.ppt
Leading on intervention: steps to a provision map, National Strategies on Teachfind
http://www.teachfind.com/national-strategies/leading-intervention-steps-provision-map
Step 1: Audit the projected need within the school
Audit and record current provision and identify resources allocated. This can initially be for a particular vulnerable group, for a particular cohort or for all children using a class base, year group or Key Stage approach.
Identify and assess the target groups. Needs could be categorised on a must/should/could help basis.
- Pupils with statutory/essential needs (must)
- Pupils whose needs impact on their progress and/or that of others (should)
- Pupils with the potential to catch up (should)
- Pupils who would benefit from provision if the budget allowed (could)
Gather information from pupils, parents, teachers and other supporting professionals.
Audit projected need, National Strategies on Teachfind
http://www.teachfind.com/national-strategies/audit-projected-need
The following link is to a planning sheet, available from the National Strategies on Teachfind, that might be useful in identifying pupils who would most benefit from help in specific areas.
Planning provision additional to Wave 1 Quality First Teaching: an example, National Archives on Teachfind (Adobe pdf file)
http://nso.archive.teachfind.com/downloader/4c4dd06346017e6b5d4d4a90e7b8bdc6.pdf
Step 2: Compare projected needs with current provision and identify staff development needs
Comparing projected needs with current provision might identify specific areas of concern; for example, a particular subject area. Alternatively, it might raise awareness of a particular group that is not as well supported as others who might be equally or even less needy.
Once specific groups or areas of concern have been recognised, staff training needs can be identified. Planning for staff development will require:
- Identification of training needs from the provision map
- Tailoring continuing professional development (CPD) to the whole school
- Class, Key Stage or year group requirements
- Teaching assistants or teachers or both
Compare projected year group needs with current provision and identify changes and staff development needs, National Strategies on Teachfind
http://www.teachfind.com/national-strategies/compare-projected-year-group-needs-current-provision-and-identify-changes-and-st
Step 3: Identify available resources
As well as the base budget, the school may have access to specific targeted grants through the Primary Strategy, Excellence in Cities, the Children's Fund or through other local sources.
Consider whether the school could combine funding streams to release provision across the school. Identify additional resources and provision provided through individual pupils' statements of SEN.
Step 4: Consider the evidence of what works and plan the provision map for next year
Review evidence on the effectiveness of:
- Teaching assistant support
- Reductions in class sizes
- Setting
- Individual learning programmes
- Interventions
Identify future resource needs: teaching personnel and teaching material, skills and specialisms and financial resources.
Two additional steps
The National Strategies flowchart (see above) for planning effective provision features two additional steps to complete the process of provision mapping and ensure the necessary evidence is collected for monitoring and evaluation of the provision map.
Step 5: Identify criteria and processes for tracking pupils’ progress and monitoring impact
Consider provision already in place within the school and whether the tracking procedure measures both small and large steps in progress.
Step 6: Establish systems for evaluating the effectiveness of your provision
Consider the following questions:
- How do you know that the provision you have planned has been effective?
- How do you evaluate the quality of your provision?
- How do you build in evaluation from the start?
- How do you involve parents/carers and pupils in the evaluation?
Establishing systems for evaluation will require:
- Building in evaluation from the start
- Effectively and consistently using assessment tools
- Developing consultation strategies with parent/carers
- Developing pupil participation strategies
Examples of provision maps
Staffordshire County Council has produced a set of example provision maps that schools could use to help them develop their own. The set also includes a sample individual education plan.
The provision maps are in a range of formats, so schools can choose what works best for them.
Examples include:
- A map of provision across a whole year
- A map of provision for cognition and learning needs in Key Stage 2
- A provision map for the Early Years Foundation Stage and Key Stage 1
- A provision map for Behavioural, Emotional, Social Development (BESD) needs, incorporating a Venn diagram to categorise overlapping types of provision
Individual education plans and provision mapping, Staffordshire County Council (Word doc file)
http://education.staffordshire.gov.uk/NR/rdonlyres/49D893DD-7178-4D1A-B1AB-3C899476B5AD/23326/IEPsandProvisionMappring.doc
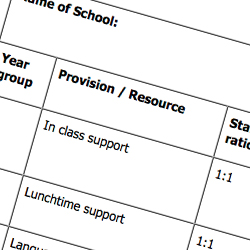
Provision maps for individual pupils
Trafford Council has produced sample provision maps for individual pupils in the primary and secondary phase.
It includes space for detailing the additional and different provision/resource the individual pupil is set to receive, the cost per week and total annual cost.
Individual provision map for a primary pupil with a statement, Trafford Council (Word doc file)
http://www.traffordlearning.org/trafford/Sections/public_html/Teaching/sen/documents/StatementSENProvisionMapPrimarye.g.complete_002.doc
Individual provision map for a secondary pupil with a statement, Trafford Council (Word doc file)
http://www.traffordlearning.org/trafford/Sections/public_html/Teaching/sen/documents/StatementSENProvisionMapSecondarye.g.complete_001.doc
Additional sources and further reading
East Riding of Yorkshire Council has produced a guide to creating a provision map, with case studies illustrating each of the seven steps.
Seven steps to a provision map, East Riding (Word doc file)
http://www.eriding.net/resources/inclusion/provision_mapping/061123_jstuart_sen_provmap_seven_steps_prim_guidelines.doc
The National Strategies' summary of research could help you identify effective and ineffective interventions.
Summary of research on effective additional provision, National Strategies on Teachfind (Word doc file)
http://nso.archive.teachfind.com/downloader/16d0daaeba95810e09f194809d631cfa.doc
EduKey provide specialist provision mapping software, which includes an IEP writer, review reminders and a large library of proven intervention strategies.